|
|
|
|
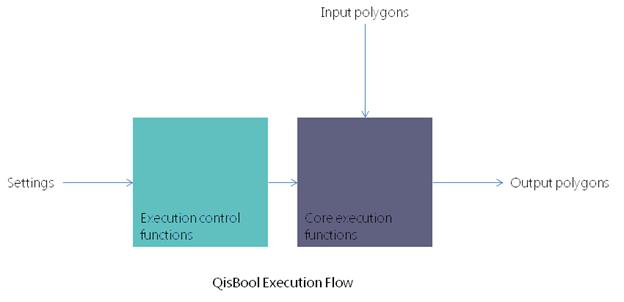
QisBool
Core Functions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To perform
Boolean operations (single threaded) such as Unary Union, Binary Union,
Difference, XOR and Intersection on up to two sets of polygons. |
|
Prototype |
|
int QisBool_Booleanize( EBooleanOp iOpCode, int** iXY1, int* iNV1, int iN1, int** iXY2, int* iNV2, int iN2, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, void* iBooleanHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
EBooleanOp iOpCode: Specifies the Boolean operation to
be performed. eUNION_OPCODE
: Unary Union on Input Set #1 eDIFFERENCE_OPCODE
: Input Set #1 - Input Set #2 (Difference) eXOR_OPCODE
: Input Set #1 XOR Input Set #2 eINTERSECTION_OPCODE
: Input Set #1 AND Input Set #2 eBINARYUNION_OPCODE
: Union of Input Set #1 and Input Set #2 b.
int iN1: Number of polygons in input set #1. c.
int* iNV1: A list of vertex numbers, one per polygon
in set #1. (For any closed polygon, number of vertices = number of sequential points + 1, the last
vertex being same as the first). d.
int** iXY1: A list of x,y co-ordinate values (number
of pairs = number of vertices) per polygon in input set #1 (For a rectangle,
there would be 5 x,y pairs or 10 integers representing x,y co-ordinates). e.
int iN2, int* iNV2, int** iXY2 : Polygons belonging to
input set #2. f.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to a QisBool object
(created using QisBool_Create). |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int* oN: Address of an integer to store the number of
output polygons. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer which will
point to a list of vertex numbers (int*) for each one of the output polygons. a.
int*** oXY: Address of a integer double-pointer which
will point to a list of x,y co-ordinate pairs for each one of the output
polygons. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
-1: Invalid (null) QisBool handle (iBooleanHandle) c.
error: error code (<0). Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get more
information about this error. d.
warning: warning code (>0). Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get more
information about this error. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
Input set #1 (iN1, iNV1, iXY1) must contain valid
polygons. b.
Except for Unary Union (eUNION_OPCODE), Input Set #2
(iN2, iNV2, iXY2) must contain valid polygons. For Unary Union, this set can
be empty (iN2=0, iNV2=NULL, iXY2=NULL). c.
iBooleanHandle must be a handle returned by QisBool_Create but not destroyed
by QisBool_Destroy. d.
If the input data sets are not very large, it is
advisable to use this function rather than the multi-threaded counterparts QisBool_UnionMT and QisBool_BinaryMT to avoid the
overhead incurred by multi-threading. e.
If either of the input data sets contains Leonov polygons, QisBool must be
notified by calling QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovInput. f.
The following functions may be called before
QisBool_Booleanize to control it's execution: QisBoolOptions_SetEnhancedValidation QisBoolOptions_SetValidationMode QisBoolOptions_SetPartitioningThreshold QisBoolOptions_SetNonIsotrSizing QisBoolOptions_SetReturnSliceEdges QisBoolOptions_SetEdgePtCompensation QisBoolOptions_SetRoundCorners QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovOutput QisBoolOptions_SetConvexOutput QisBoolOptions_SetTestManhattan g.
To avoid any un-intended side-effects from a previous
run, it is advisable to call QisBoolOptions_Reset first to clear
the internal settings before setting up the options (aforementioned
functions) for this operation. |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function performs the specified operation on
Input Set #1 and Input Set #2 and allocates new memory to store the output
polygons. b.
This operation is single-threaded. |
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
If successful (return code 0), oN, oNV and oXY
represent output polygons. If oN is 0, this set is empty. If an error occurs (return
code < 0) the output data set is invalid. b.
If the function returns a warning (return code >
0), it indicates that an error occurred at certain co-ordinates. Call QisBool_GetIllegalPolygonIndices to get the
location of those co-ordinates. c.
Since this function (if successful) allocates new
memory to store data corresponding to the output polygons (oN, oNV, oXY), it
is the client program's responsibility to free this memory by calling QisBool_Release, otherwise a
memory leak will occur. This data is valid and can be used until it is freed
using QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int IQisBool::Booleanize( EBooleanOp iOpCode, int** iXY1, int* iNV1, int iN1, int** iXY2, int* iNV2, int iN2, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
perform multi-threaded Unary Union on a set of polygons. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_UnionMT( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int*** oXY,
int** oNV, int* oN, short iNThreads, void* iBooleanHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int iN: Number of polygons in the input set. b.
int* iNV: A list of vertex numbers, one per polygon in
the set. (For any closed polygon, number of vertices = number of sequential points + 1, the last
vertex being same as the first). c.
int** iXY: A list of x,y co-ordinate values (number of
pairs = number of vertices) per polygon in the input set (For a rectangle,
there would be 5 x,y pairs or 10 integers representing x,y co-ordinates). d.
short iNThreads: Number of threads to be used to
unionize the data. e.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to a QisBool object
(created using QisBool_Create). |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int* oN: Address of an integer to store the number of
output polygons. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer which will
point to a list of vertex numbers (int*) for each one of the output polygons. b.
int*** oXY: Address of a integer double-pointer which
will point to a list of x,y co-ordinate pairs for each one of the output
polygons. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
-1: Invalid (null) QisBool handle (iBooleanHandle) c.
error: error code (<0). Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get more
information about this error. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
The input set
(iN, iNV, iXY) must contain valid polygons. b.
iBooleanHandle must be a handle returned by QisBool_Create but not destroyed
by QisBool_Destroy. c.
If the input data set is very large, it is advisable
to use this function rather than the single-threaded counterpart QisBool_Booleanize. In doing so, the
number of threads should be used judiciously taking into consideration the
processing power (multiple cores, hyper-threading) of the underlying hardware. d.
If the input data set contains Leonov polygons, QisBool must be
notified by calling QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovInput. e.
The following functions may be called before
QisBool_Booleanize to control its execution: QisBoolOptions_SetEnhancedValidation QisBoolOptions_SetValidationMode QisBoolOptions_SetPartitioningThreshold QisBoolOptions_SetNonIsotrSizing QisBoolOptions_SetReturnSliceEdges QisBoolOptions_SetEdgePtCompensation QisBoolOptions_SetRoundCorners QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovOutput QisBoolOptions_SetConvexOutput f.
To avoid any un-intended side-effects from a previous
run, it is advisable to call QisBoolOptions_Reset first to clear
the internal settings before setting up the options (aforementioned
functions) for this operation. |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function unionizes the polygons in the input set
and allocates new memory to store the output polygons. b.
This function might fail of the number of instances of QisBool in use exceed a
certain pre-defined internal limit. The thread management for the purpose of
executing this function is handled internally and should be invisible to the
client code. |
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
If successful (return code 0), oN, oNV and oXY
represent output polygons. If oN is 0, this set is empty. If an error occurs
(return code < 0) the output data set is invalid. b.
Since this function (if successful) allocates new
memory to store data corresponding to the output polygons (oN, oNV, oXY), it
is the client program's responsibility to free this memory by calling QisBool_Release, otherwise a
memory leak will occur. This data is valid and can be used until it is freed
using QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int IQisBool::UnionMT( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int*** oXY,
int** oNV, int* oN, short iNThreads ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
perform multi-threaded Boolean operations such as Difference, XOR and
Intersection on up to two sets of polygons. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_BinaryMT( int** iXY1, int* iNV1, int iN1, int** iXY2, int* iNV2, int iN2, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, short iNThreads, EBooleanOp iOpCode, void*
iBooleanHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
EBooleanOp iOpCode: Specifies the Boolean operation to
be performed. eUNION_OPCODE
: Unary Union on Input Set #1 eDIFFERENCE_OPCODE
: Input Set #1 - Input Set #2 (Difference) eXOR_OPCODE
: Input Set #1 XOR Input Set #2 eINTERSECTION_OPCODE
: Input Set #1 AND Input Set #2 eBINARYUNION_OPCODE
: Union of Input Set #1 and Input Set #2 b.
int iN1: Number of polygons in input set #1. c.
int* iNV1: A list of vertex numbers, one per polygon
in set #1. (For any closed polygon, number of vertices = number of sequential points + 1, the last
vertex being same as the first). d.
int** iXY1: A list of x,y co-ordinate values (number
of pairs = number of vertices) per polygon in input set #1 (For a rectangle,
there would be 5 x,y pairs or 10 integers representing x,y co-ordinates). e.
int iN2, int* iNV2, int** iXY2 : Polygons belonging to
input set #2. f.
short iNThreads: Number of threads to be used to
unionize the data. g.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to a QisBool object
(created using QisBool_Create). |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int* oN: Address of an integer to store the number of
output polygons. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer which will
point to a list of vertex numbers (int*) for each one of the output polygons. c.
int*** oXY: Address of a integer double-pointer which
will point to a list of x,y co-ordinate pairs for each one of the output
polygons. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
-1: Invalid (null) QisBool handle (iBooleanHandle) c.
error: error code (<0). Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get more
information about this error. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
Input sets #1 and #2 must contain valid polygons. b.
iBooleanHandle must be a handle returned by QisBool_Create but not destroyed
by QisBool_Destroy. c.
If the input data set is very large, it is advisable
to use this function rather than the single-threaded counterpart QisBool_Booleanize. In doing so, the
number of threads should be used judiciously taking into consideration the
processing power (multiple cores, hyper-threading) of the underlying hardware. d.
If either of the input data sets contains Leonov polygons, QisBool must be
notified by calling QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovInput. e.
The following functions may be called before
QisBool_Booleanize to control it's execution: QisBoolOptions_SetEnhancedValidation QisBoolOptions_SetValidationMode QisBoolOptions_SetPartitioningThreshold QisBoolOptions_SetNonIsotrSizing QisBoolOptions_SetReturnSliceEdges QisBoolOptions_SetEdgePtCompensation QisBoolOptions_SetRoundCorners QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovOutput QisBoolOptions_SetConvexOutput f.
To avoid any un-intended side-effects from a previous
run, it is advisable to call QisBoolOptions_Reset first to clear
the internal settings before setting up the options (aforementioned
functions) for this operation. |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function performs the specified operation on
Input Set #1 and Input Set #2 and allocates new memory to store the output
polygons. b.
This function might fail of the number of instances of QisBool in use exceed a
certain pre-defined internal limit. The thread management for the purpose of
executing this function is handed internally and should be invisible to the
client code. |
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
If successful (return code 0), oN, oNV and oXY
represent output polygons. If oN is 0, this set is empty. If an error occurs
(return code < 0) the output data set is invalid. b.
Since this function (if successful) allocates new memory
to store data corresponding to the output polygons (oN, oNV, oXY), it is the
client program's responsibility to free this memory by calling QisBool_Release, otherwise a
memory leak will occur. This data is valid and can be used until it is freed
using QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int
IQisBool:: BinaryMT( int** iXY1, int* iNV1, int iN1, int** iXY2, int* iNV2, int iN2, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, short iNThreads, EBooleanOp iOpCode ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
|
© 2012 Artwork Conversion
Software Inc. |
|
|
417 Ingalls St. Santa Cruz CA
95060 |
|
|
[T] +1 831-426-6163 [F] +1
831-[E] info@artwork.com |
|